In the vast landscape of financial services, where verdant fields of bustling economic activity thrive, there exist barren zones known as banking deserts. These are not literal deserts, but rather metaphorical ones, defined by their scarcity of physical bank branches. The phenomenon raises crucial questions about access, opportunity, and the evolving nature of financial ecosystems. As we delve into the concept of a banking desert, we will explore its implications on local populations, the role of digital banking in bridging these voids, and how communities can foster financial inclusivity. This exploration is not just academic; it is essential for understanding a pivotal challenge in today’s socio-economic fabric. Join us on a journey to uncover the intricacies and impacts of banking deserts, a crucial step towards nurturing a more inclusive financial future.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Concept of a Banking Desert
- Exploring the Causes Behind the Emergence of Banking Deserts
- The Impact of Banking Deserts on Local Communities
- Technological Solutions to Combat Banking Deserts
- Government and Policy Interventions to Address Banking Scarcity
- The Role of Community Banks and Credit Unions
- Future Trends: The Shift Towards Digital Banking
- How Consumers Can Adapt to Living in a Banking Desert
- Case Studies: Successful Overcoming of Banking Deserts in Various Regions
- Recommendations for Stakeholders to Mitigate Banking Desert Challenges
- Q&A
- The Conclusion

Understanding the Concept of a Banking Desert
In areas where traditional banking services are sparse or altogether absent, residents face significant challenges. These regions, often termed as banking deserts, are primarily characterized by their lack of physical bank branches. This scarcity can lead to reduced economic activities and financial inclusivity, hampering both personal and community growth.
The impact of living in a banking desert is profound:
- Limited access to credit and loans, which affects personal financial growth and restricts small businesses from expanding or even initiating.
- Increased reliance on non-traditional financial services like payday lenders, which often charge exorbitant interest rates.
- Difficulty in managing everyday financial activities which many urban dwellers take for granted, such as depositing or withdrawing cash, and accessing financial advice.
Understanding the geographical spread and the demographics affected by banking deserts can help in formulating targeted interventions. Below is a simple overview showing areas commonly classified as banking deserts in the UK:
| Region | Percentage of Population Affected |
|---|---|
| Northern Ireland Rural Areas | 25% |
| North East England Countrysides | 20% |
| Scottish Highlands | 22% |
Efforts to bridge the gap in financial services, such as the introduction of mobile banking units or stronger broadband for online banking, are essential in these areas. Only through concerted efforts and innovative solutions can these financial deserts be transformed into fertile grounds for economic development and prosperity.
Exploring the Causes Behind the Emergence of Banking Deserts
Banking deserts, areas with limited or no access to traditional banking services, are increasingly prevalent in both urban and rural settings. This phenomenon primarily arises from a convergence of economic and strategic decisions made by financial institutions. One central factor is the cost-efficiency drive among banks which leads to the closure of less profitable branches. Particularly affected are low-income neighborhoods and sparsely populated areas where transactions and account balances may not justify the overhead of physical branches.
Another catalyst for the spread of banking deserts is the rapid evolution of banking technology. As more consumers shift towards online and mobile banking, physical branches become less necessary for the banks’ operations. However, this shift assumes that all customers have access to internet services and are also willing to transition to digital banking solutions. Below are key points highlighting technology’s impact:
- Digital competence: Older populations often face challenges adapting to digital platforms.
- Internet accessibility: Rural and impoverished areas may lack reliable internet access, necessary for online banking.
Economic shifts also play a significant role. The following table provides a snapshot of economic factors contributing to banking deserts:
| Economic Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Local economic decline | Reduces the profitability of maintaining bank branches. |
| Banking sector consolidation | Fewer banks in the marketplace increase the probability of branch closures. |
These economic elements, compounded by strategic bank decisions and technological advancements, create a challenging environment for maintaining traditional banking infrastructures in susceptible areas.
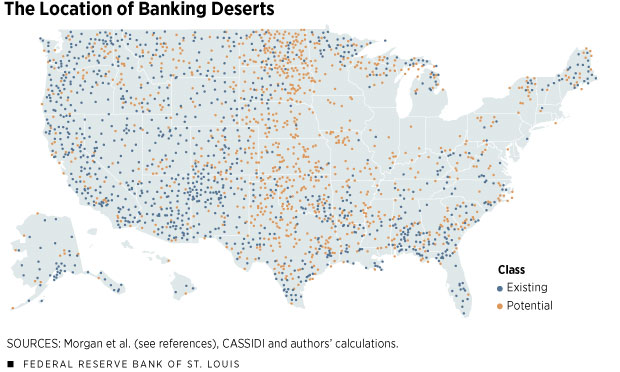
The Impact of Banking Deserts on Local Communities
In regions where traditional banking services are sparse or absent, the economic and social fabric begins to experience noticeable strains. Often termed banking deserts, these areas do not have easy access to physical bank locations, impacting various aspects of life, from personal finance management to business operations. The consequences of living in a banking desert extend beyond mere inconvenience, affecting the local community economically and interpersonally.
Economic Effects: Communities lacking banking services often face heightened economic hardships. The absence of nearby reputable financial institutions means that residents may turn to alternative financial services, such as payday loans, which can carry exorbitant interest rates and fees. This can lead to a cycle of debt and financial instability. Furthermore, small businesses in these areas struggle to flourish without access to banking services like loans and credit lines which are essential for growth and stability.
- Increased reliance on non-traditional financial services
- Higher rates of financial instability among residents
- Reduced growth and development opportunities for local businesses
Social Implications: The absence of banks in a community also carries deep social repercussions. Banks often serve as critical hubs where individuals not only conduct transactions but also seek advice and consult on financial matters. Without this, there is a palpable decline in financial literacy among residents. Additionally, the lack of physical banking locations tends to discourage personal saving, further escalating economic vulnerability among community members.
| Impact | Consequence |
|---|---|
| High usage of predatory services | Increased personal debt |
| Lack of financial literacy | Poor financial planning and management |
| Low personal savings | Reduced economic resilience |
Addressing the challenges posed by banking deserts requires targeted efforts both from policymakers and financial institutions to embed more robust banking networks and alternative financial services that can cater to underserved communities efficiently and ethically.

Technological Solutions to Combat Banking Deserts
In areas where traditional banking facilities are sparse or completely absent, individuals face significant challenges in accessing basic financial services. This phenomenon, often occurring in both urban neighborhoods and rural areas, impacts economic opportunities and overall community development. However, advancements in technology are beginning to bridge this gap, offering innovative solutions to those living in these underserviced regions.
One of the most impactful technological interventions is the deployment of mobile banking units. These are essentially banks on wheels that travel to different locations, providing essential services like depositing, withdrawing, and account management. Moreover, digital banking platforms have surged in popularity, allowing users to perform financial transactions right from their smartphones or computers. Below is a list of ways technology is making a difference:
- ATM Installations – Deploying more ATMs in underserved locations.
- E-Banking Apps – Developing user-friendly banking apps with features tailored to the needs of individuals in remote areas.
- Financial Literacy Tools – Offering online educational resources to help improve financial knowledge and decision-making.
Furthermore, collaboration between tech companies and traditional banks has resulted in more inclusive financial products tailored for those without easy access to banking facilities. The following table highlights some of the recent partnerships aimed at combating banking deserts:
| Tech Company | Bank | Initiative |
|---|---|---|
| FinTech Innovators Inc. | Big Bank Co. | Mobile Banking Expansion |
| Digital Solutions Ltd. | Community Bank | Enhanced E-Banking App |
| NetBanking Startups | Region Trust | ATM Network Growth |
These initiatives not only provide vital banking services but also foster a sense of financial inclusion and empowerment among the residents of banking deserts. As technology evolves, the potential to completely eradicate these deserts grows, promising a financially connected and supported global community.
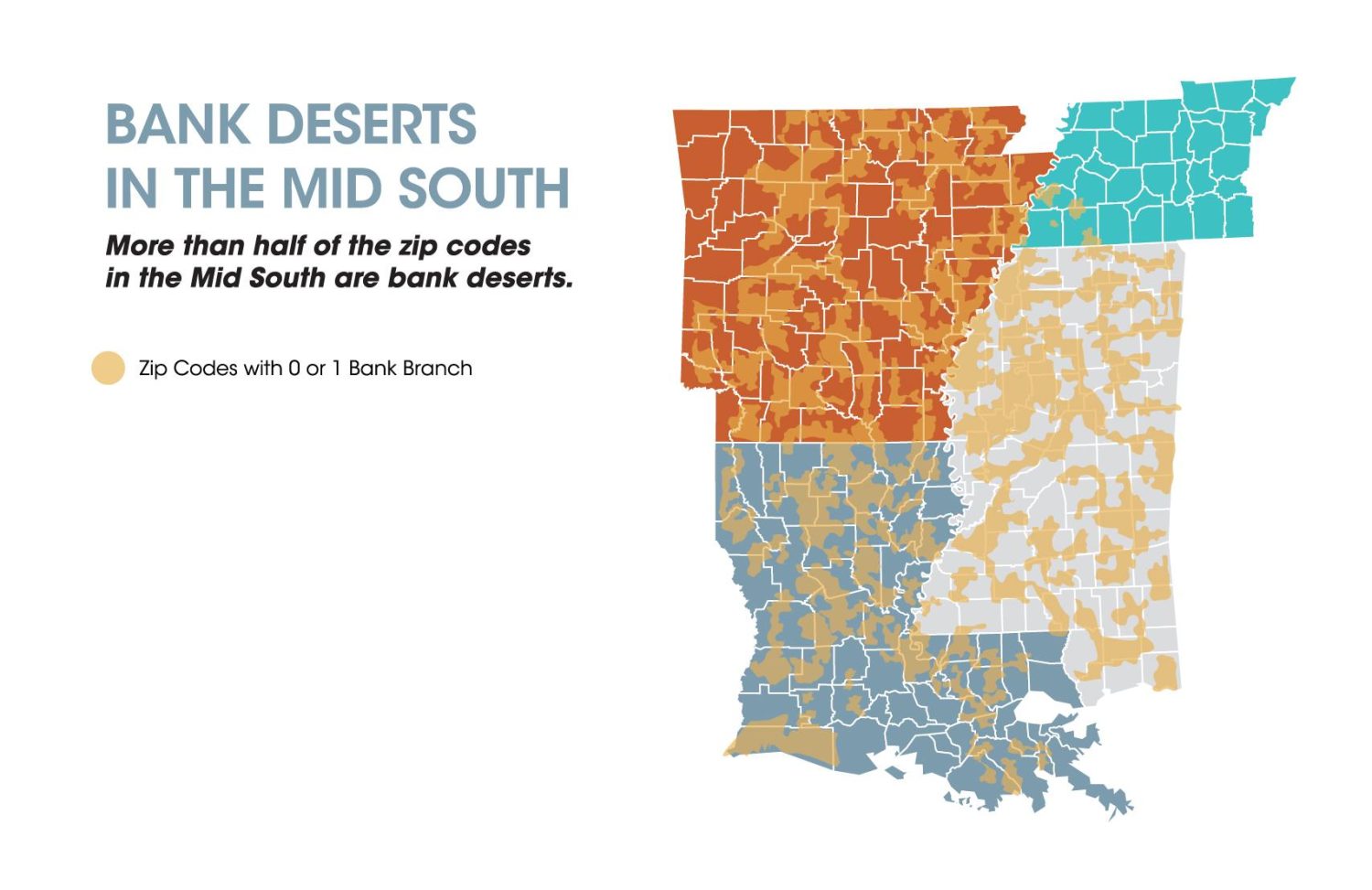
Government and Policy Interventions to Address Banking Scarcity
In regions recognized as banking deserts, where access to physical bank branches is minimal or non-existent, government and policy intervention plays a crucial role in bridging the financial inclusion gap. One common approach is the initiation of mobile banking units. These units are equipped to travel to underserved areas, offering essential banking services like deposit withdrawal, account opening, and financial advice directly to the residents’ doorstep.
Financial incentives for banks that establish branches in these underserved areas have also proven effective. These may include:
- Tax breaks for banks opening new branches in designated banking deserts
- Grants or subsidies to support operational costs in less profitable areas
- Reduced regulatory requirements specific to banking desert regions
Moreover, collaborations between traditional banks and fintech companies are encouraged through policies fostering innovative banking solutions. One initiative might be the shared ATMs concept, where several banks share the operating cost of ATMs placed in strategic, yet underserved locations to ensure broader access to cash:
| Location | Number of ATMs | Banks Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Carpenter’s Village | 2 | 4 |
| Old Town | 3 | 5 |
| East Bay | 1 | 3 |
These strategies, when combined, create a supportive ecosystem that not only addresses the immediate issue of banking scarcity but fosters long-term financial empowerment and inclusion.
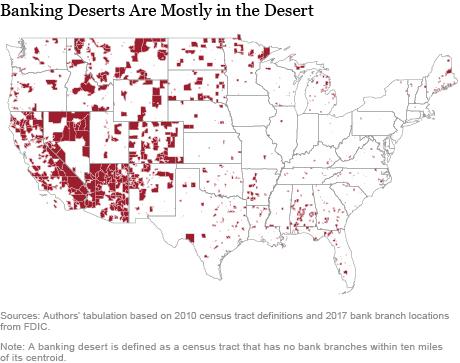
The Role of Community Banks and Credit Unions
In regions identified as banking deserts, where traditional bank branches are few and far between, community banks and credit unions serve as crucial lifelines. These institutions often step in to fill the void left by larger banks, offering essential financial services to underserved populations. Their unique position allows them to provide more personalized banking experiences and foster closer relationships with community members.
Community banks and credit unions differ in their structure and operations:
- Community Banks: Typically locally owned and operated, these banks invest heavily in local economies by extending loans that help spur local business activities. Their decision-making processes are deeply rooted in understanding the local needs, which allows greater flexibility in offering financial products tailored to those specific needs.
- Credit Unions: These member-owned financial cooperatives are often praised for their lower fees and customer-friendly loan rates. Unlike banks that aim to drive profit for shareholders, credit unions return surplus income to their members in the form of dividends, reduced fees, or improved services.
In helping combat the challenges of banking deserts, the role of technology has also been pivotal. Many community banks and credit unions have started adopting digital banking solutions to extend their reach without physical branches. This strategy not only helps in providing continuous access to banking services but also ensures that financial inclusion is achievable even in the most remote areas.
| Service | Community Bank | Credit Union |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Loan Rates | Competitive | Often Lower |
| Customer Service | Highly Personalized | Member-focused |
| Investment in Local Economy | Significant | Moderate |
As both types of institutions hone their focus on technological integration, the hope of turning banking deserts into fertile grounds for financial growth and inclusivity brightens. This, coupled with their inherent community-centric approach, positions community banks and credit unions as pivotal players in bridging the financial gap in underserved regions.
Future Trends: The Shift Towards Digital Banking
As traditional brick-and-mortar banks become increasingly scarce in certain regions, the concept of a ’banking desert’ becomes more prevalent. These areas, often in low-income or rural communities, lack sufficient access to physical bank branches. The implications are profound as residents in these regions struggle with heightened barriers to financial services, potentially exacerbating economic disparities.
Technology, however, is stepping into this void with digital banking solutions, emerging as a pivotal force reshaping access to financial services. The advent of online and mobile banking platforms offers a lifeline to those in banking deserts, ensuring that basic banking operations—deposits, withdrawals, transfers—are still within reach. The trends indicate a digital leap with the following promising advancements in the banking sector:
- Mobile-First Banking: Platforms that prioritize mobile use are becoming the norm, not the exception. This not only extends banking reach but also enhances user convenience and accessibility.
- FinTech Partnerships: Traditional banks are increasingly collaborating with FinTech companies to broaden service offerings and penetrate underserved markets.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are being leveraged to provide personalized financial advice directly to users’ smartphones, a crucial service in areas without local bank branches.
This paradigm shift heralds a significant transformation where the physical presence of banks may no longer dictate financial inclusivity. Instead, the focus will likely be on the robustness and reach of digital solutions, potentially redrawing the financial landscape and making ‘banking deserts’ a thing of the past.
How Consumers Can Adapt to Living in a Banking Desert
In areas sparsely populated by financial institutions, or “banking deserts,” consumers often face significant challenges accessing traditional banking services. Innovative solutions and proactive behaviors, however, can assist individuals in navigating these financial voids efficiently.
One major lifeboat for those in banking deserts is the surge of digital banking platforms. These online entities usually require just a smartphone or computer with internet access to operate. Strategically embracing technology can thus grant convenient access to functionalities generally offered by physical banks including fund transfers, bill payments, and direct deposits. Here are several steps to adapt:
- Online Banks: Opt for banks that provide comprehensive online services.
- Mobile Apps: Leverage apps from reputable financial entities to accomplish everyday banking.
- Fintech Platforms: Exploit technologies like e-wallets and peer-to-peer payment systems.
For retail financial needs, community resources can also be lifesavers. Local credit unions typically offer lower fees and interest rates, which can alleviate the financial burdens faced by residents of banking deserts. Partnering with these community-based institutions can provide not only basic banking services but also support local economic growth.
| Resource Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Online Banks | 24/7 access, no branch visits required |
| Credit Unions | Lower fees, community focus |
| Fintech Services | Fast transactions, innovative tools |
Incorporating these adaptations not only helps in managing personal finances but also prepares consumers for a more digitized global economy. Thus, while banking deserts present significant hurdles, they also offer an opportunity to pioneer the bridge to a tech-savvy financial future.
Case Studies: Successful Overcoming of Banking Deserts in Various Regions
In the fight against banking deserts, several regions have adopted innovative approaches to ensure their populations have access to essential financial services. One standout example is the mobile banking initiative launched in rural Scotland. Faced with the closure of physical bank branches, mobile banks now travel to remote villages according to a set weekly schedule, offering a lifeline for everyday banking activities. This initiative not only provides conventional banking services but also education on digital banking tools to enhance financial literacy.
In another approach, the city of Birmingham tackled the banking desert issue by partnering with local credit unions. This alliance aimed to establish more accessible financial points in underserved areas, offering no-fee ATM services and financial advisory workshops. Residents not only gained easier access to cash withdrawals but also benefited from crucial financial guidance, helping to foster a culture of informed financial decisions.
| Region | Strategy | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Rural Scotland | Mobile Banking Units | Increased access, enhanced financial literacy |
| Birmingham | Credit Union Partnership | Better access, improved financial education |
These success stories reflect a broader movement towards innovative, localized solutions that address the challenges of banking deserts, ensuring communities retain essential financial services and support. As each region tailors its approach based on specific needs and resources, such dynamic strategies are crucial in bridging the financial accessibility gap.

Recommendations for Stakeholders to Mitigate Banking Desert Challenges
In the face of rising banking deserts, stakeholders must adopt strategic measures to ensure that communities maintain access to necessary financial services. A robust approach involves enhancing the presence and functionality of digital banking solutions. Stakeholders are encouraged to invest in the development and deployment of user-friendly mobile banking applications and online platforms that can serve as adequate substitutes for physical bank branches. Additionally, educating the public on how to effectively utilize these tools can help mitigate the adverse effects of banking deserts.
Collaborative efforts between governments, financial institutions, and non-profit organizations can also play a crucial role in addressing the issue. Possible initiatives include:
- Subsidizing transportation for residents in banking deserts so they can access banking services located further away.
- Establishing temporary mobile banking units that periodically visit underserved areas to offer critical financial services.
- Encouraging banks to adopt a shared branching model where multiple financial institutions share a physical space to provide their services, reducing overall operational costs.
Here is an outline of potential community banking hubs where stakeholders could pilot shared services, reducing both cost and geographic barriers:
| Location | Services Offered | Participating Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Barkstone Area | ATMs, Deposit Services, Financial Advice | Bank A, Bank B |
| MidGrove Lane | Loan Processing, Account Set-up | Bank C, Bank D |
| Eastwood Village | Savings Plans, Mortgage Services | Bank E, Bank F |
Initiating these strategies should help bridge the financial service gaps created by banking deserts and ensure more communities have reliable access to banking solutions.
Q&A
**Q: What exactly is a banking desert?**
A: Much like a natural desert is scarce in water, a banking desert is an area sparse in financial institutions. These regions are void of easy access to traditional banking services such as branches or ATMs, making financial transactions and personal finance management considerably more challenging for residents.
Q: How does an area become a banking desert?
A: Banking deserts typically emerge through a blend of economic and social factors. These can include the consolidation of large banks, which might close less profitable branches in rural or low-income areas, or a lack of financial profitability in certain regions, discouraging new branches from opening.
Q: Who is most affected by banking deserts?
A: The impact predominantly resonates with low-income families and small businesses in the affected areas. The lack of physical banks can limit their access to lending services, safe deposit facilities, and other financial services, which are essential for economic health and personal financial growth.
Q: Are there any solutions to counteract banking deserts?
A: Yes, several strategies are being explored. These include encouraging the establishment of community banks and credit unions which are more likely to serve the needs of local residents. Technological solutions, such as mobile banking and fintech innovations, are also growing in popularity as they can provide crucial banking services without the need for physical bank branches.
Q: What can ordinary people do if they find themselves in a banking desert?
A: Individuals living in banking deserts can look towards alternative financial services. Mobile banking, online banking platforms, and fintech applications can offer many of the services found at traditional banks. It’s also beneficial for individuals to seek financial literacy resources to explore how to best navigate their banking options effectively.
The Conclusion
As we journey through the shifting sands of the financial landscape, the phenomenon of banking deserts remains a critical area for exploration and understanding. These barren financial zones remind us of the evolving nature of banking access, and the urgent need to address the scarcity that impacts vulnerable communities. We hope this article has provided a comprehensive oasis of knowledge, shedding light on what banking deserts are, why they exist, and their profound implications. In our continuous endeavor to educate and inform, we encourage our readers to reflect on how inclusive financial solutions can be cultivated to ensure that no one is left stranded in a banking desert. For further insights and updates on financial inclusivity and other economic developments, remain engaged with our ongoing discourse. Let us chart a course toward a future where financial services blossom in every corner of society.