In the intricate tapestry of the financial world, depositories play a pivotal role, often unnoticed yet indispensable. They are the silent sentinels guarding the assets of millions, from intricate securities to the simplest of bonds. In this article, we delve into the very essence of what depositories are, embarking on a journey to uncover their definition, understand their multifaceted roles, explore the various types that exist, and elucidate with real-world examples. Whether you are a seasoned investor, a curious student, or simply a keen learner of economic structures, join us as we demystify these crucial yet often overlooked institutions in the global financial landscape.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of a Depository in the Financial System
- Exploring the Core Definitions: What Exactly is a Depository
- Diving Deeper: The Various Types of Depositories
- Key Functions and Responsibilities of Depositories
- Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Depository Institutions
- The Impact of Depositories on Market Efficiency
- Evaluating the Safety Measures Within Depository Operations
- Future Trends: Technological Advancements in Depository Services
- Choosing the Right Type of Depository for Your Investments
- Best Practices for Interacting with a Depository
- Q&A
- In Conclusion
Understanding the Role of a Depository in the Financial System
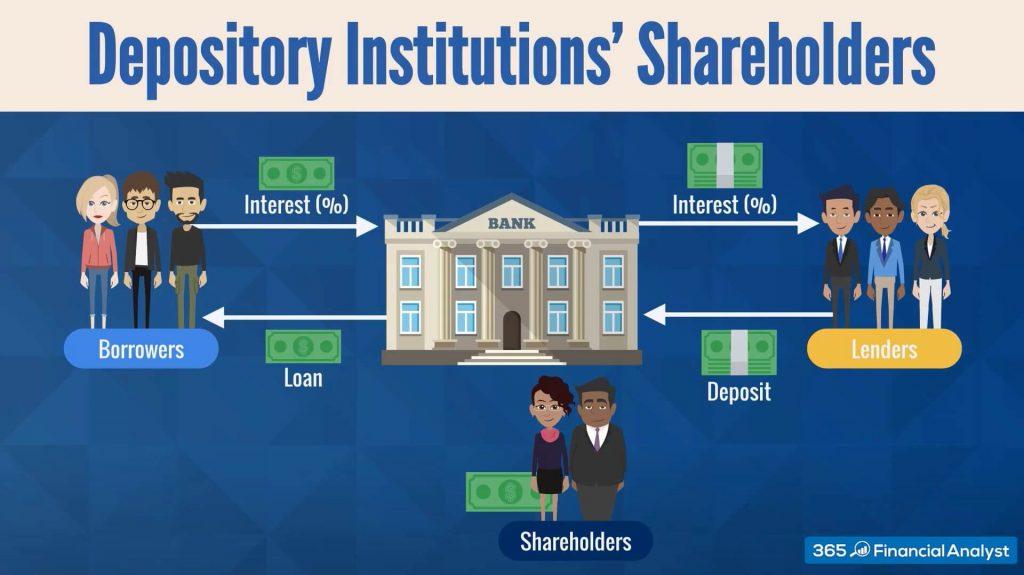
A depository plays a critical role in the financial landscape by holding securities such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds and facilitating the smooth execution of transactions. It acts as a safeguard for these securities, ensuring their safety and accuracy, while also assisting in the seamless transfer from seller to buyer. This is vital for maintaining investor confidence and promoting a stable financial market environment.
There are generally two types of depositories:
- Central depositories: These hold the securities of multiple companies and manage the trades on a large scale, often nationally.
- Commercial depositories: These cater to individual financial institutions, handling securities specifically held and traded by them.
Examples of major depositories include:
| Central Securities Depository | Region Served |
| DTCC (Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation) | USA |
| CDSL (Central Depository Services Limited) | India |
| Euroclear | Europe |
The advantages provided by depositories include lower risks of theft or loss of securities, quicker and more cost-effective transactions, and the convenience of holding securities in an electronic or “dematerialized” form. This facilitates easier tracking and management of investments, which is crucial for both individual investors and institutional traders. By ensuring transparency and efficiency, depositories contribute fundamentally to the health and operation of the financial market.
Exploring the Core Definitions: What Exactly is a Depository
In the intricate web of financial terminology, a depository stands as a fundamental institution that safeguards securities to ensure smooth and secure transactions. At its essence, this entity holds and administers securities, such as stocks or bonds, on behalf of investors, which can range from individual retail participants to large institutional entities. One can view a depository as a safe vault where investors’ assets are stored and protected from potential threats like theft or loss.
The pivotal role of a depository in the financial ecosystem facilitates numerous services beyond mere storage. It provides services such as the settlement of transactions, record maintenance, and ensuring the swift execution of trading orders. To facilitate a clearer understanding, let us outline the primary functions in an unnumbered list:
- Settlement of Trades: Ensuring the delivery of securities is completed efficiently and correctly.
- Maintenance of Records: Keeping meticulous records of transactions and holdings for each account.
- Transfer of Ownership: Facilitating the transfer of securities between buyer and seller, maintaining the integrity and legality of each transaction.
Given the broad range of activities and responsibilities, depositories play an indispensable role in the vigor and stability of the securities market. Their seamless operation is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring a robust financial market infrastructure.
Diving Deeper: The Various Types of Depositories
Exploring the landscape of depositories reveals a diversity designed to meet various investor needs and regulatory frameworks. Primarily, there are two types of depositories: central depositories and commercial depositories. Each plays a crucial role in the financial markets by ensuring the security and efficiency of transactions.
Central Depositories act as the backbone of a country’s securities trading system. They hold securities such as stocks, bonds, and other financial assets in electronic form. More importantly, they enable transactions to be processed swiftly and securely between parties. Prime examples include the Central Securities Clearing System (CSCS) in Nigeria and the Depository Trust Company (DTC) in the United States. Central depositories reduce risk in the financial markets, providing a stable environment for trading and investments.
- Commercial Depositories, on the other hand, are often divisions of larger banking institutions, catering directly to individual investors and companies. They safeguard financial assets such as securities and facilitate an array of transactions including deposits, withdrawals, and loan processing. Their services are tailored to enhance the liquidity and capital efficiency for their clients.
- Another type worth noting is the International Depositories, which specialize in handling transactions involving foreign securities. Institutions such as Euroclear and Clearstream stand out in this category, serving as crucial nodes in the global financial infrastructure.
The table below provides a quick comparison of the primary functions and examples of each depository type:
| Depository Type | Primary Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Central | Settlement of market trades, maintenance of central securities register | DTC (USA), CSCS (Nigeria) |
| Commercial | Asset safeguarding, transaction facilitation | HSBC, Citibank |
| International | Handling foreign securities transactions | Euroclear, Clearstream |
Understanding these various types of depositories empowers investors and institutions alike to make informed decisions about where to house their assets, based on their specific financial activities and needs.
Key Functions and Responsibilities of Depositories
In the complex landscape of financial markets, depositories play a pivotal role by safeguarding securities and ensuring their smooth and efficient transfer. They function as a central location where electronic records of stock, bonds, and other assets are maintained, effectively reducing the risk of loss associated with physical certificates. Additionally, they facilitate the clearing and settlement of trades, helping to streamline operations and minimize the risks involved in trading securities.
Key roles include:
- Record Maintenance: Depositories keep detailed, updated electronic records of all transactions, holdings, and changes in ownership of securities. This meticulous record-keeping is vital for the accuracy of market data and investor confidence.
- Transfer of Ownership: They handle the transfer of securities between accounts, which occurs without the physical exchange of documents, by book-entry. This process is critical during buying and selling, ensuring that transactions are executed smoothly.
- Corporate Actions: Depositories also manage corporate actions like mergers, stock splits, and dividend distributions, ensuring that benefits reach rightful shareholders without discrepancies.
Beyond these functions, their role extends to assisting in collateral management by providing services related to the pledging of securities. They also play a significant part in dematerialization, the process of converting physical shares into electronic form, which is fundamental for modern trading. Here’s a simple overview:
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Demat | Converting physical certificates to electronic data |
| Trading | Assisting in the seamless exchange of securities |
| Settlement | Ensuring successful completion of transactions |
| Corporate Action | Administering dividends, mergers, etc. |
With their multifunctional activities, depositories underpin market stability and protect the interests of investors, making them an indispensable component of the financial sector landscape.

Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Depository Institutions
In the complex world of finance, depository institutions play a pivotal role. These entities, tasked with accepting deposits from customers, reflect a broad spectrum of operation and service types. Below, we explore a few fascinating case studies that illuminate their functioning and impact on the everyday financial landscape.
Example 1: Retail Banking Transformation
One notable British bank, traditionally a brick-and-mortar establishment, recently transitioned into a fully digital platform. This shift not only expanded their customer base but also redefined user experience by integrating mobile banking features. Such innovations have made it easier for customers to perform real-time transactions and manage their finances more efficiently.
Example 2: Credit Unions Empowering Local Communities
Consider the case of a small credit union in Northern England, which focuses particularly on financial inclusivity. By offering microloans and other tailored financial products, this institution has significantly contributed to local business growth, helping stimulate economic progress within the community.
- Enhanced user features through digital interfaces
- Community-focused financial solutions fostering local economies
- Strategic adaptation to evolving market needs and technological advancements
These examples underscore the adaptability and essential role of depository institutions in sculpting the financial ecosystem. Whether transforming through technology or empowering local economies, these institutions continue to evolve, meeting the diverse needs of their clientele.
The Impact of Depositories on Market Efficiency
Depositories play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of the market through several key mechanisms. Firstly, they reduce the costs associated with trading. By electronically managing the ownership records of securities, depositories eliminate the need for physical certificates, thus cutting down paperwork and associated costs considerably. This streamlined approach minimizes the risk of errors and delays related to manual handling and processing of stock certificates.
Improvement of liquidity is another significant impact. Depositories enable the quick transfer of securities between accounts, which can be completed within hours compared to the days it may take to transfer physical certificates. Rapid transfers increase the willingness of participants to trade, thereby boosting liquidity in the market. Additionally, the assurance of title and elimination of forged or duplicate certificates increase investor confidence and market participation.
- Enhanced security measures reduce systemic risks, protecting against fraud.
- Acceleration of settlement cycles turbocharges market operations.
- Diversification of investment portfolios becomes simpler and more feasible.
Below is a simple table showcasing the types of securities handled by depositories:
| Type of Security | Examples |
|---|---|
| Equities | Shares, Stocks |
| Debt Securities | Bonds, Debentures |
| Derivatives | Options, Futures |
The integral role of depositories in fostering a dynamic and efficient market environment is irrefutable. By providing a safe, reliable system for the handling of securities, they not only enhance trading but also contribute to the overall stability of the financial system.
Evaluating the Safety Measures Within Depository Operations
In the realm of finance, safeguarding assets within depositories is paramount. Depositories, entrusted with the management and safekeeping of securities, implement rigorous controls to prevent fraud and mismanagement. Understanding these protective measures can enhance investor confidence and ensure the integrity of financial transactions.
Risk Management Frameworks are crucial in monitoring and mitigating potential threats within depository operations. These frameworks typically involve:
- Continuous risk assessment to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Implementation of state-of-the-art security systems to thwart cyber-attacks and physical breaches.
- Regular audits both internal and external, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and revealing any procedural weaknesses.
Operational Controls also play a significant role; they include:
- Strict access controls to sensitive data and physical vaults.
- Comprehensive training programs for employees to heighten awareness about security protocols.
- Multi-tiered authentication processes for transaction authorization, reducing the risk of unauthorized asset transfers.
Moreover, technological advancements are continually integrated into depository systems to enhance safety measures. The table below illustrates a simple comparison between traditional and technologically advanced safety measures:
| Feature | Traditional Measures | Technological Advances |
|---|---|---|
| Security Systems | Manual checks | AI-driven surveillance |
| Audit Processes | Periodic manual audits | Continuous automated audits |
| Data Access | Limited digital access | Biometric authentication |
These layers of security ensure that depository operations are conducted within a tightly controlled environment, minimizing the risks associated with asset storage and transactions.

Future Trends: Technological Advancements in Depository Services
The financial sector is spearheading impressive strides in technological innovation, particularly within depository services. As we look towards the future, it’s evident that advancements like blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) are poised to redefine the mechanisms of deposit functions and security management. Blockchain technology, renowned for its decentralization and security features, is projected to bring about transparent, tamper-proof systems that could drastically minimize fraud and enhance efficiency in depository transactions.
AI and Machine Learning have also begun to make their mark, primarily through automated and highly sophisticated algorithms capable of predicting market trends and managing vast amounts of data to reduce risks and increase accuracy in record-keeping. Here are some of the key technological trends expected to transform depository services:
- Digital ledgers: Implementation of distributed ledger technology for real-time transaction records.
- Enhanced cybersecurity: Employing advanced encryption methods and cybersecurity protocols to safeguard sensitive information.
- Smart contracts: Utilization of self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing transaction speeds.
The integration of these technologies not only promises greater operational efficiency but also offers improved user experiences. Financial institutions that adapt promptly to these innovative technologies are likely to lead the race, setting new industry standards and redefining the user interaction with depository services.
Choosing the Right Type of Depository for Your Investments
When it comes to safeguarding your investments, selecting the appropriate type of depository is crucial. It boils down to understanding the different options available and how each can align with your financial goals and requirements. Broadly, the choices split into two categories: Central Securities Depositories (CSDs) and Depository Receipts (DRs).
Central Securities Depositories (CSDs) are specialized financial entities which hold and administer securities to facilitate exchange. CSDs are typically chosen for more extensive, often institutional, investments ensuring smoother transactions. They maintain the security and integrity of title transfers. Investors benefit from reduced costs due to their efficient handling and minimized need for physical documentation.
- Direct CSDs: Your securities are held directly with the CSD, providing full transparency and fast access.
- Indirect CSDs: Your investments are held via a custodian bank that liaises with the CSD, adding an extra layer of oversight.
Depository Receipts (DRs), including American Depository Receipts (ADRs) and Global Depository Receipts (GDRs), represent ownership in foreign stocks and are ideal for diversifying your investment portfolio internationally. These provide a perfect channel for individuals or entities wishing to invest outside their home jurisdiction without direct transactions in foreign markets, thereby simplifying trading and potentially mitigating geopolitical risks.
| Type | Geographical Focus | Ideal for |
|---|---|---|
| ADR | United States | Investors wanting to invest in non-US companies via US stock exchanges |
| GDR | Global | Investors seeking worldwide exposure without specific market focus |
Understanding these differences allows you to better choose a depository that fits your investment strategy, whether you’re focusing on domestic markets with a CSD or looking globally with DRs. Reflect on your objectives and consult with a financial advisor to make the most informed decision.

Best Practices for Interacting with a Depository
When managing your interactions with a depository, it’s crucial to maintain a streamlined process to ensure both safety and efficiency. First, ensure that all your documents and securities are prepared and organized before you begin transactions. A well-documented portfolio can significantly speed up depository operations and minimize errors or delays.
Develop a habit of regular communication. Keeping in constant touch with your depository will not only keep you updated about any changes in depository procedures but also strengthen the trust and cooperative relationship. Furthermore, always verify all transactions for accuracy. This action helps in prompt resolution of any discrepancies and thus safeguards your assets effectively.
| Action | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Document Organization | Label all files clearly and maintain a digital copy. |
| Regular Communication | Schedule monthly check-ins and request transaction reports. |
| Transaction Verification | Double-check all entries and rectify any errors immediately. |
Focusing on these strategies will enhance your depository interactions, making them more secure, traceable, and user-friendly. Implementing these methods will not only keep your transactions fluid but also save time and resources, thus optimizing your overall investment operations.
Q&A
### Q&A Section: Understanding Depositories
Q1: What is a depository?
A depository is a facility or institution that safely stores and manages securities like stocks, bonds, and other financial assets for investors. These can include banks, trust companies, or specific financial organizations authorized to hold and protect these assets. The main purpose of a depository is to ensure the security of the securities held and to facilitate a more efficient transaction process.
Q2: Can you explain what “meaning” holds in the context of a depository?
In financial terms, the “meaning” of a depository revolves around its role as a guardian and facilitator in the financial market. It means security, reliability, and efficiency in handling transactions of securities. It acts as a central location where securities transactions can be processed seamlessly, providing a smooth flow of financial assets in the market.
Q3: What are the primary types of depositories?
There are two main types of depositories: centralized and decentralized. Centralized depositories, often known as traditional depositories, hold the physical or electronic records of securities and related transactions. Decentralized depositories, on the other hand, utilize technologies like blockchain to distribute records across a network, enhancing security and transparency without a central authority.
Q4: Could you give some examples of depositories?
Sure! A prominent example of a centralized depository in the UK is the Central Securities Depository (CSD). Internationally, examples include the Depository Trust Company (DTC) in the United States and Clearstream in Europe. For decentralized models, platforms like Ethereum can act as depositories for digital assets and cryptocurrencies through their blockchain technology.
Q5: How do depositories impact investors and the overall financial market?
Depositories play a crucial role in bolstering investor confidence and market stability by ensuring secure and efficient management and transfer of securities. They reduce the risk of loss or theft and streamline operations by eliminating the need for physical handling of documents. This efficiency contributes to more dynamic and robust financial markets.
Q6: Are there any specific regulations governing depositories?
Yes, depositories are typically subjected to strict regulatory frameworks to protect the interests of investors and maintain market integrity. In the UK, for instance, depositories operate under regulations enforced by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). These regulations ensure that depositories adhere to high standards in terms of security, transparency, and operational conduct.
Q7: What future trends might affect depositories?
With the continuous evolution of technology, especially blockchain and artificial intelligence, depositories are expected to see significant transformations. The future may bring more decentralized models, enhancing security and operational efficiency, potentially reshaping how securities transactions are managed globally.
Q8: Where can aspiring investors get more information about using depositories?
Aspiring investors can consult financial advisors, read materials from financial regulatory bodies, or visit the official websites of various depositories and financial institutions to get detailed and authoritative information. Education is key in understanding how these institutions contribute to a healthy investment environment.
In Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration into the realm of depositories, we hope this article has illuminated both their foundational roles and practical applications in the financial ecosystem. From safeguarding assets to enhancing transaction efficiency, depositories are pivotal in shaping the stability and fluidity of markets. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a finance student, understanding these institutions and their functionalities provides a critical lens through which to view and engage with the broader economic landscape. May this guide serve as a solid stepping stone for your future financial endeavors and discussions. Remember, in the intricate world of finance, knowledge is not just power—it is security and opportunity combined. Continue to explore, question, and learn.


